The Asian International Arbitration Centre Malaysia AIAC sits in one of Malaysias most iconic buildings Bangunan Sulaiman. In 1963 North Borneo and Sarawak joined the Federation of Malaysia.

Afp News Agency On Twitter South China Sea Philippines South China
1 This Act shall apply throughout Malaysia.

. Arbitration is an ADR process which has some similarities to a court hearing- it is a dispute which is resolved by an arbitrator usually an independent third party whose role is similar to a judges. Basic procedural principles or mandatory rules to be applied by arbitral tribunal. Some court judgments are published court papers can be publicly accessible via online file search and trials are usually heard in open court which means any member of the public can observe the proceedings.
The Malaysian Arbitration Act 2005. Prior to that the main piece of legislation governing pre-trial resolution of commercial disputes in the state of Malaysia was the 1952 Arbitration Act hereinafter referred to as the AA. Arbitration proceedings in Malaysia are governed by the Arbitration Act 2005 Act.
The intimacy in an arbitration process which what makes it better than litigation. Pursuant to section 38 of the AA an award made in Malaysia or any other state which is a contracting party to the New York Convention is recognised and enforceable in Malaysia. Thu Mar 19 162745 2020.
The Act distinguishes between domestic and international arbitration. In comparison arbitration is a private process. It is governed by the Arbitration Act 2005.
Arbitration differs from actual court proceedings whereby both parties in the dispute can decide. The definition of an arbitration agreement is contained in section 9 of the AA and discussed in Section 361 below. Today many business people in Malaysia and company owners choose this process as an alternative to court litigation.
Depending on what process is set forth in the Rules that govern your arbitration the AAA invites an arbitrator or arbitrators to serve on the case. 2020 1 MLJ lix Arbitration and its Development in Malaysia. 2 Act 2018 an arbitration agreement is regarded.
As part of this process the arbitrator reviews case information checks for conflicts and returns a signed oath document along with any relevant disclosures if applicable. For more information on arbitration please see our earlier article. While sharing the same objective as court proceedings ie.
2 In respect of a domestic arbitration where the seat of arbitration is in Malaysia. Over the last decade major parties have made considerable attempts to promote Malaysia as a seat of arbitration. The process gained more popularity after the Arbitration Act was updated.
The Malaysian Arbitration is a multidisciplinary arbitration chamber who represents both the claimant and respondent in arbitration proceeding. Legislation governing arbitration in Malaysia is quiet archaic which is why the countrys government has recently taken steps to make it more compliant with UNCITRAL. Based in Kuala Lumpur our multilingual network of consultants have represented clients from all over Malaysia and South-East Asian in arbitration proceeding under the auspices of Asian International.
The AIAC Mediation Rules 2018 is a set of. Here are five things you should know about arbitration in Malaysia. Section 3 3 b removes the application of Part III of the Act to an international arbitration unless the parties agree otherwise in writing.
Application to arbitrations and awards in Malaysia. The informal settings of arbitration in Malaysia over formalities followed in a courtroom are preferable at any time. Formerly known as Kuala Lumpur Regional Centre for Arbitration KLRCA.
The principal legislation that applies to both domestic and international arbitration in Malaysia is the Arbitration Act 2005 Arbitration Act which is closely modelled on the UNCITRAL Model Law. A Parts I II and IV of this Act shall apply. Court proceedings are potentially a public affair.
The Arbitration Act 1952 2 is silent on the issue of. B Part III of this Act shall apply unless the parties agree otherwise in writing. Because Malaysia is an international business center and English is widely spread many arbitrators are fluent in English and offer their services to.
If this option is triggered then the Director of the AIAC that will appoint a suitable arbitrator to hear and determine the. On 1 November 1972 Malaysia adopted the arbitration laws prevailing in Sabah and Sarawak and it became known as the Arbitration Act 1952 1952 Act which is based on the English 1950 Act. An amendment to the 1952 Act on 1 February 1980 gave special status to arbitrations.
Following the amendments to section 9 of the Arbitration Act 2005 by virtue of the Arbitration Amendment No. The aim is to resolve a dispute arbitration is a private process that is done without a judge and can even be completed in your office meeting room. No Job Name PAGE.
Arbitration proceedings in Malaysia are governed by the Arbitration Act 2005 the Act. Party Autonomy is Key but it could come with a price. Since the coming into force of the Arbitration Act in March 2006 there have been three rounds of amendments to the Arbitration Act with the latest.
Arbitration is confidential. In Malaysia it is common for arbitration clauses to designate the Asian International Arbitration Centre formerly known as the Kuala Lumpur Regional Centre for Arbitration AIAC as the appointing authority. Arbitration is sometimes seen as an attractive alternative to the court process especially in certain industries or where there is an international element to the dispute.
An arbitration must be in writing. Moreover arbitrators tend to settle and satisfy both parties in the best possible way.

Malaysia Ten Key Changes To The Aiac Arbitration Rules Baker Mckenzie Insightplus

Pharmaboardroom Product Liability Malaysia

In A Tense Environment In South China Sea The Possibility Of Miscalculations Is High As Philippine Pres Aquino Said He Ma South China Sea Philippines Vietnam

The Search Area 2 24 Million Square Nautical Miles Of Malaysianairlines Flight Mh370 Is Roughly The Size Of Continental Us Malaysian Airlines Monon Baghdad

Pakistan Maritime Claims About Outer Limits Of Its Continental Shelf Iilss International Institute For Law Of The S Continental Shelf Maritime Imaginary Maps
An Overview Of Mediation Under The Pusat Mediasi Covid 19 Trials Appeals Compensation Malaysia
An Overview Of Mediation Under The Pusat Mediasi Covid 19 Trials Appeals Compensation Malaysia

Explore Our Sample Of Separation And Property Settlement Agreement Template For Separation Agreement Separation Agreement Template Divorce Settlement Agreement
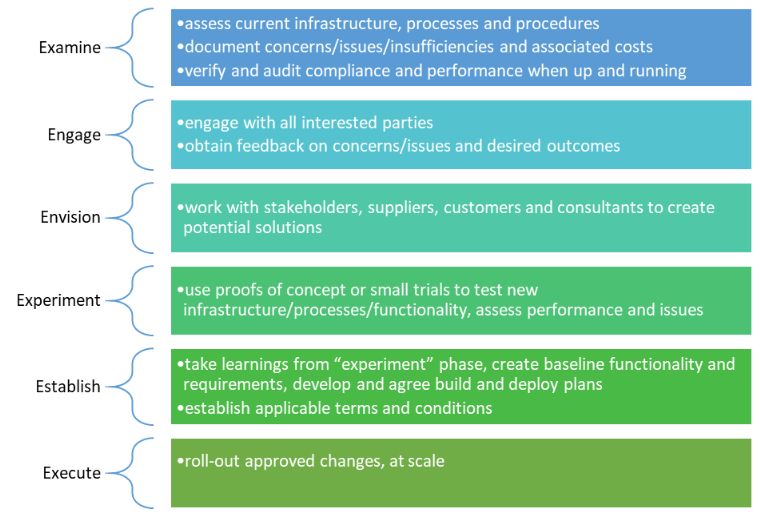
The 6 E S Of The Digital Transformation Journey It And Internet Uk

Winding Up Vs Arbitration No To Stay But Court Has Discretion To Dismiss The Winding Up

Adjudication Under Cipaa Act 2012 Malaysia Cipaamalaysia Com

Process Flow Chart On Arbitration Of Construction Claims Dispute Pdf

Arbitration Act 2005 Laws Of Malaysia Act 646
An Overview Of Mediation Under The Pusat Mediasi Covid 19 Trials Appeals Compensation Malaysia
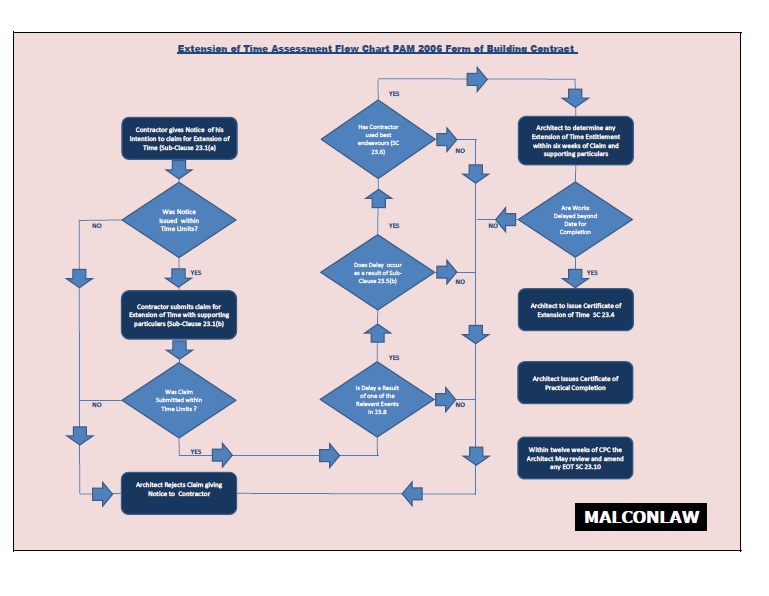
Eot Malaysian Construction And Contract Law
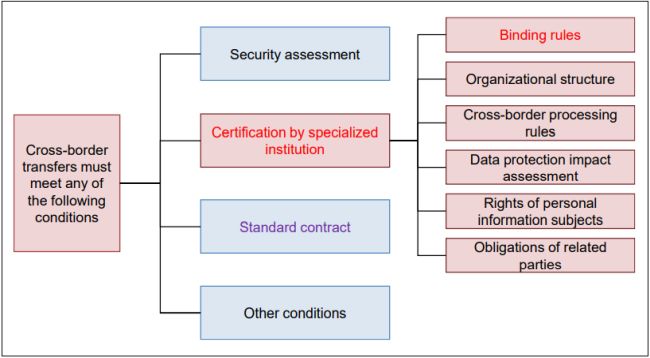
Specifications For Certification Of Personal Information Export Data Protection China

Asian International Arbitration Centre Aiac Official Launch Of The Aiac I Arbitration Rules 2021 Highlights Facebook By Asian International Arbitration Centre Aiac The Aiac Was Delighted To

America Canada France Visa Jobs Dubai Oman Qattar Bahrain Kuwait Germoney Japan China Malaysia Forex Training Forex Distance Learning

Process Of Dispute Resolution In Construction Projects Through Arbitration Semantic Scholar
